By: AY1920S2-CS2103-T09-2 Since: Feb 2020 Licence: MIT
1. Introduction
iTrack Pro is for the grocery shop owners to keep track of the products, customers, and transactions of the shop and have a better understanding of the business by viewing the performance of products and behaviors of customers. It is also able to provide an analysis of the entire business to help the owner manage the shop.
2. Quick Start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
iTrackPro.jarhere. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your Inventory System.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
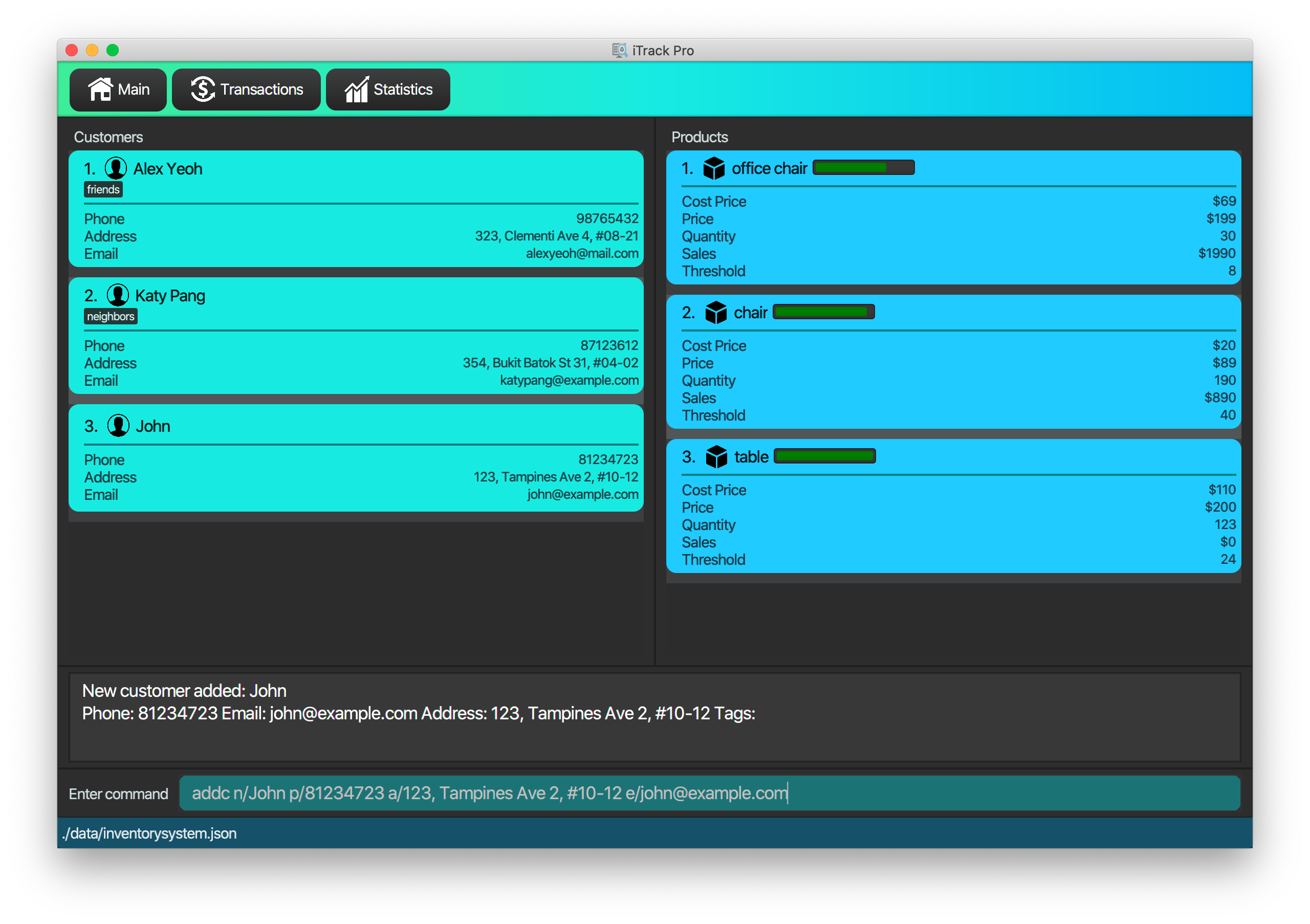
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Some example commands you can try:
-
listc: lists all customers -
addcn/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01: adds a customer to the application -
deletec3: deletes the 3rd customer shown in the current list -
exit: exits the app
-
-
Refer to Section 4, “Features” for details of each command.
3. Legend
Please take note of the three different types of notification that are used in the features section:
| This tells you some things to take note of. It also helps to explain why we did what we did. |
| This provides tips on using the command the best way, and alternatives that can be used. |
| Pay attention to the warnings before you execute the command, or else things may not go according to what you expect. |
4. Features
Command Format
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional e.g
n/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
Parameters can be in any order e.g. if the command specifies
n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable.
4.1. General
4.1.2. Receiving notification while a certain product is running low.
Pops up notification if quantity of product is below threshold.
Displays the product name and remaining product quantity.
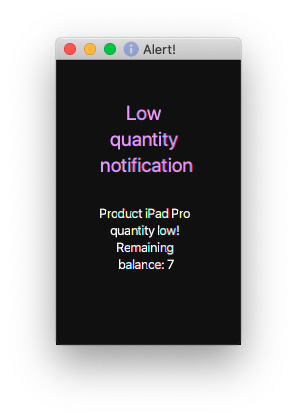
| This is a passive feature. |
4.1.3. Exiting from the program : exit
Exits from the program, closes all opened windows.
Format: exit
4.1.4. Saving the data
The application data is saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
| There is no need to save manually. |
4.1.5. Reusing previous inputs
The application keeps the history of previous inputs that was keyed in the command line.
| The history is deleted after application closes. |
4.1.6. Keeping track of products that are running low on stock
The product list updates and sorts by the progress bar indicator when user uses the listp command.
Products are ordered by the level of progress bar indicator. (E.g. the lower the bar, the higher it is in the list).
This is to help the user easier to know which products are running low on stock.

|
This is a passive feature. Green: stock > 60% Yellow: 40% < stock < 60% Orange: 20% < stock < 40% Red: stock < 20% |
4.2. Manage customers
4.2.1. Adding a customer: addc
Adds a customer to the customer list
Format: addc n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
|
The email field [e/] is optional, and will be recorded as N/A if left empty. The address field [a/] is optional, and will be recorded as N/A if left empty. |
Examples:
-
addc n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 -
addc n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/1234567 t/criminal
4.2.2. Listing all customers: listc
Shows a list of all customers in the customer list.
Format: listc
4.2.3. Editing a customer: editc
Edits an existing customer in the customer list.
Format: editc INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
Examples:
-
editc 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com
Edits the phone number and email address of the 1st customer to be 91234567 and johndoe@example.com respectively. -
editc 2 n/Betsy Crower t/
Edits the name of the 2nd customer to be Betsy Crower and clears all existing tags.
4.2.4. Finding customers: findc
Finds customers whose attributes match the given attributes.
Format: findc [n/NAME [NAME]…] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS [ADDRESS]…]
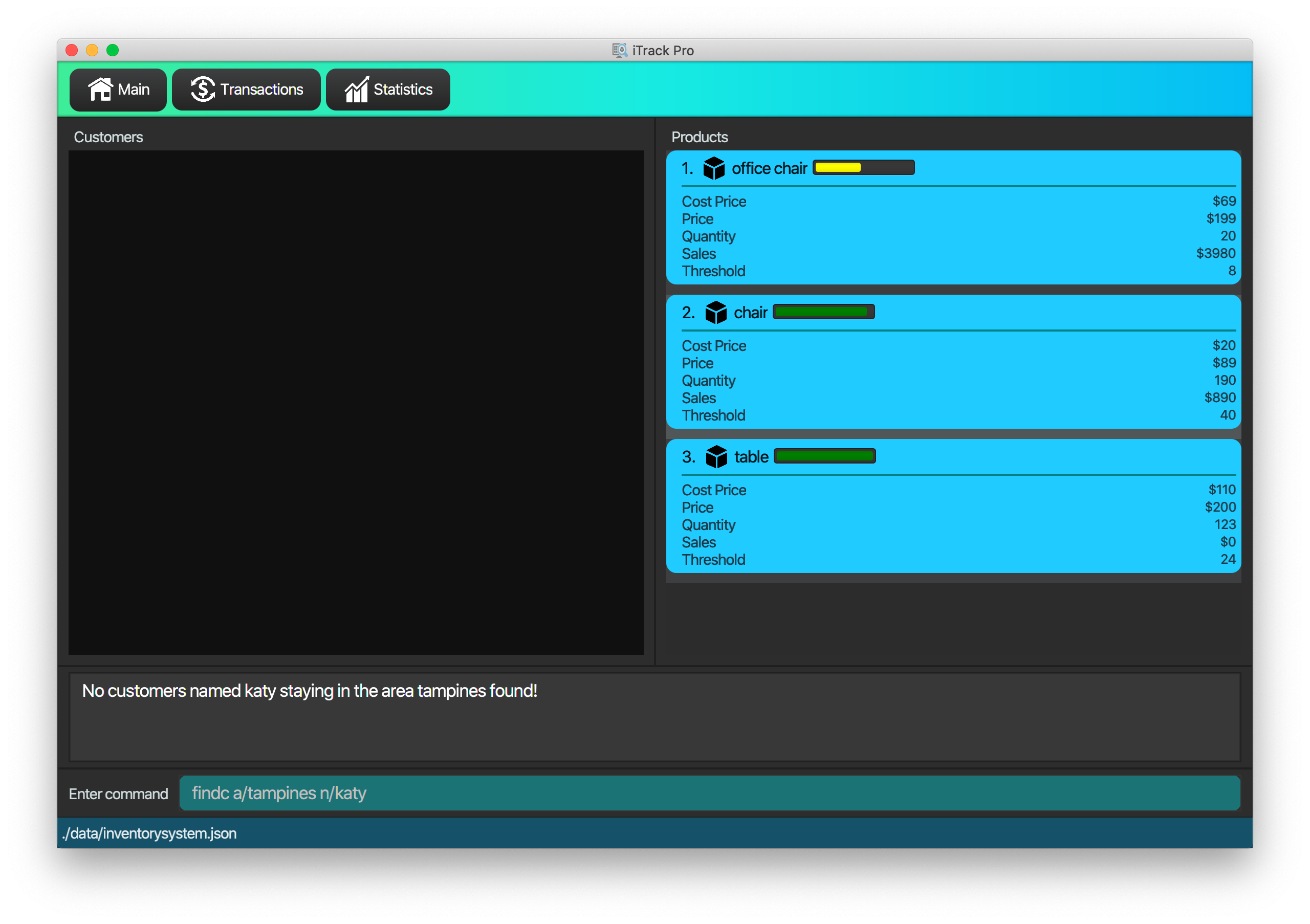
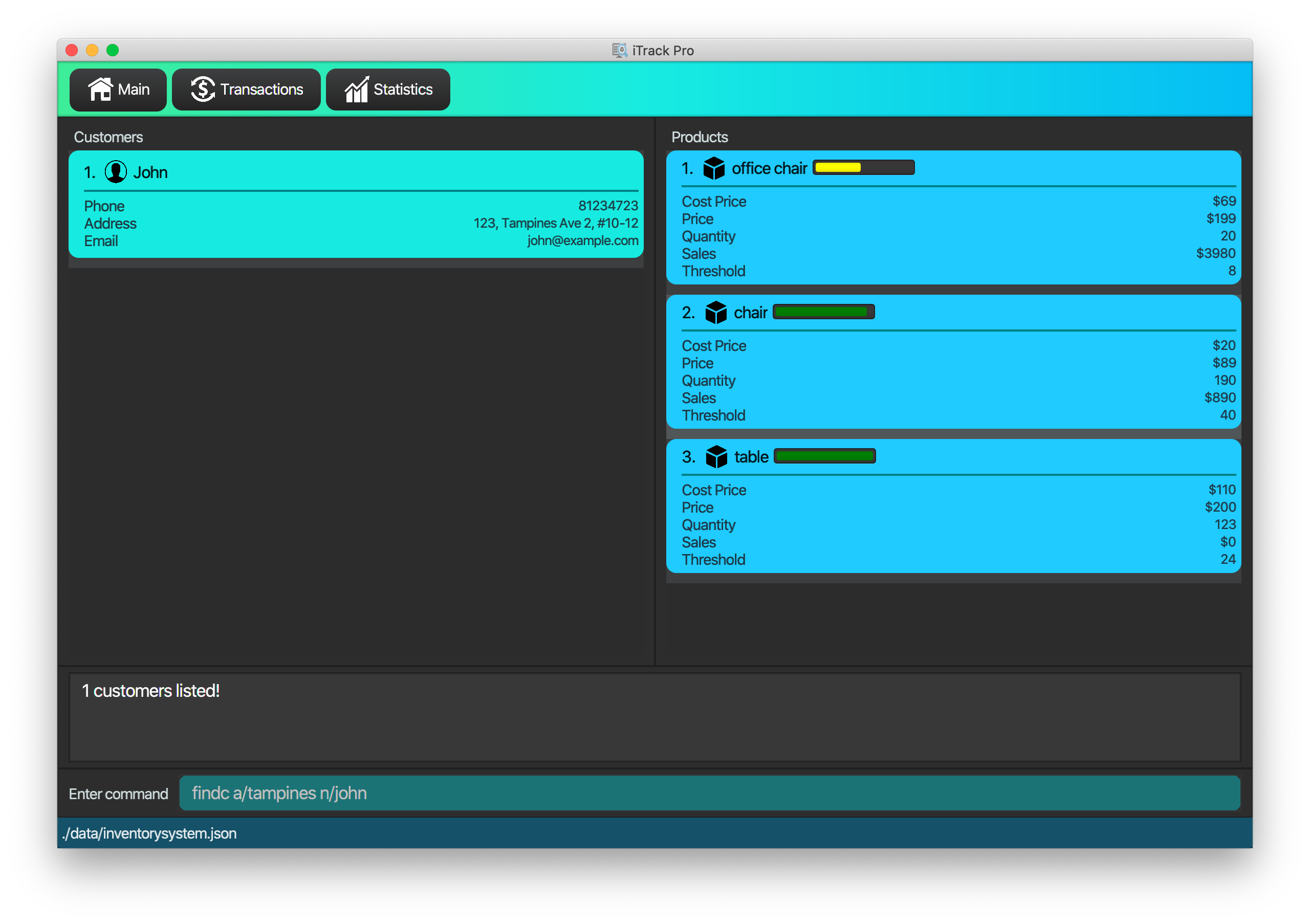
| Only name and address support multiple keywords |
Examples:
-
findc n/John
Returns all customers with names John from the customer list. -
findc n/Betsy Tim John
Returns any customer having names Betsy, Tim, OR John in the customer list. -
findc a/serangoon n/Bob
Returns all customers with addresses in Serangoon AND Bob in their names.
4.2.5. Deleting a customer: deletec
Deletes the specified customer from the customer list that is currently being displayed.
Format: deletec INDEX
| Deletes transactions that are associated with this particular customer as well. |
Examples:
-
listc
deletec 2
Deletes the 2nd customer in the customer list. -
findc n/Betsy
deletec 1
Deletes the 1st customer in the results of the find command.
4.2.6. Clearing all customers: clearc
Clears all entries from the customer list.
Format: clearc
|
Permanently deletes all the stored customer data in the application. Deletes all transactions as well. |
4.3. Manage product
4.3.1. Adding a product: addp
Adds a product to the product list.
Format: addp d/DESCRIPTION pr/PRICE q/QUANTITY cp/COSTPRICE [s/SALES]
| The default threshold value is 20% of quantity of product. |
| A product created without providing values for sales (in SGD) will be created with 0 sales. |
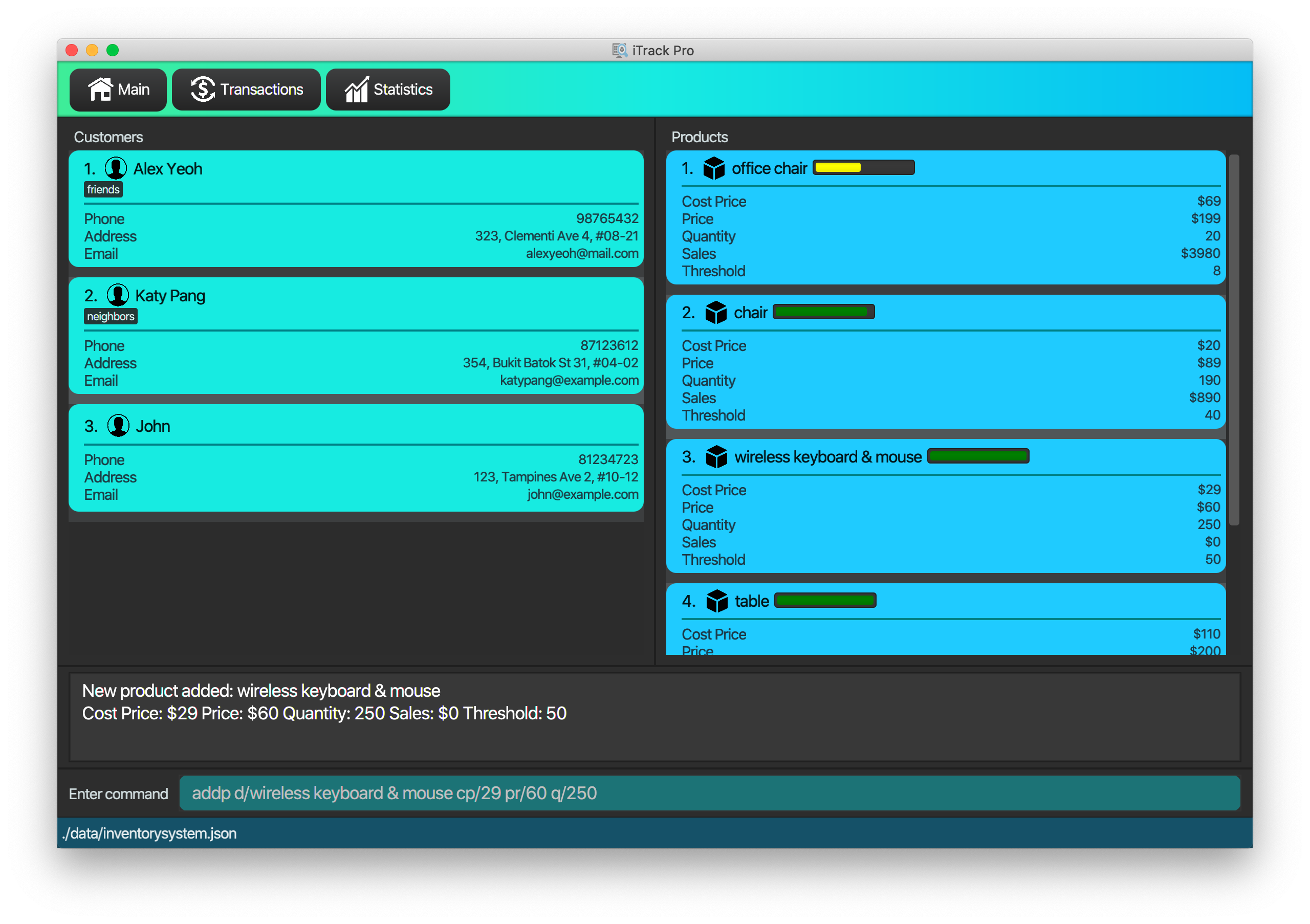
Examples:
-
addp d/iphone x pr/1000 q/10 cp/300 -
addp d/camera pr/2000 q/90 s/100 cp/1000
4.3.2. Listing all products : listp
Show all products in the product list.
Format: listp
| Sorts all of the product by the product quantity, represented by the bar indicator beside the product name. |
4.3.3. Editing a product : editp
Edits an existing product in the displayed product list.
Format: editp INDEX [d/DESCRIPTION] [pr/PRICE] [q/QUANTITY] [cp/COSTPRICE] [s/SALES]
Examples:
-
editp 1 pr/1150 q/80
Edits the price and quantity of the 1st product in the list to be $1150 and 80 respectively. -
editp 2 s/1000
Edits the sales of the 2nd product in the list to be $1000.
4.3.4. Finding products : findp
Finds products whose description contains a certain keyword
Format: findp KEYWORD [KEYWORD]…
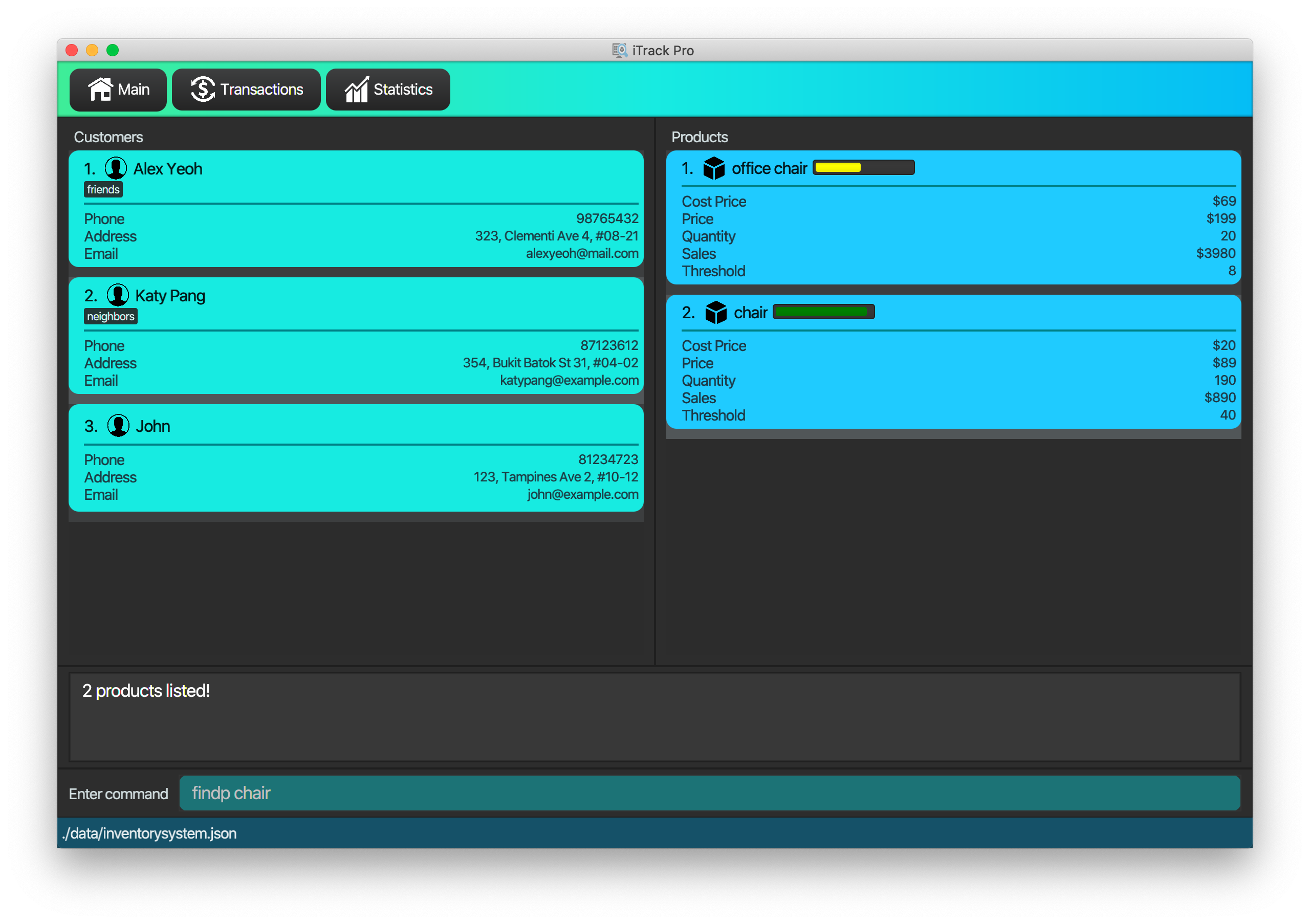
Examples:
-
findp camera
Returns all product with descriptioncamerain it. -
findp iphone
Returns all product with descriptioniPhonein it.
4.3.5. Deleting a product : deletep
Deletes the specified product from the system.
Format: deletep INDEX
| This action deletes transactions that are associated with this particular product as well. |
Examples:
-
listp
deletep 2
Deletes the 2nd product in the product list. -
findp camera
deletep 1
Deletes the 1st product in the results of the find command.
4.3.6. Clearing all products : clearp
Clears all entries from the product list.
Format: clearp
|
Permanently deletes all the stored product data in the application. Deletes all transactions as well. |
4.4. Transaction
User can navigate to the transaction panel by clicking on the transactions tab.
4.4.1. Adding a transaction : addt
Adds a specified transaction to the system.
Format: addt p/PRODUCT_ID c/CUSTOMER_ID q/QUANTITY [dt/DATETIME] [m/MONEY] [d/DESCRIPTION]
|
The date time field [dt/] is optional, and will be recorded as current local machine time if left empty. The money field [m/] is optional, and will be recorded as product price multiplied by quantity if left empty. Only need to enter if necessary (i.e. discounts on products). The description field [d/] is optional, will be recorded as N/A if left empty. Only need to enter if user wants to add notes to the transaction. |
| Adding transaction will update the quantity and sales of its associated product as well. |
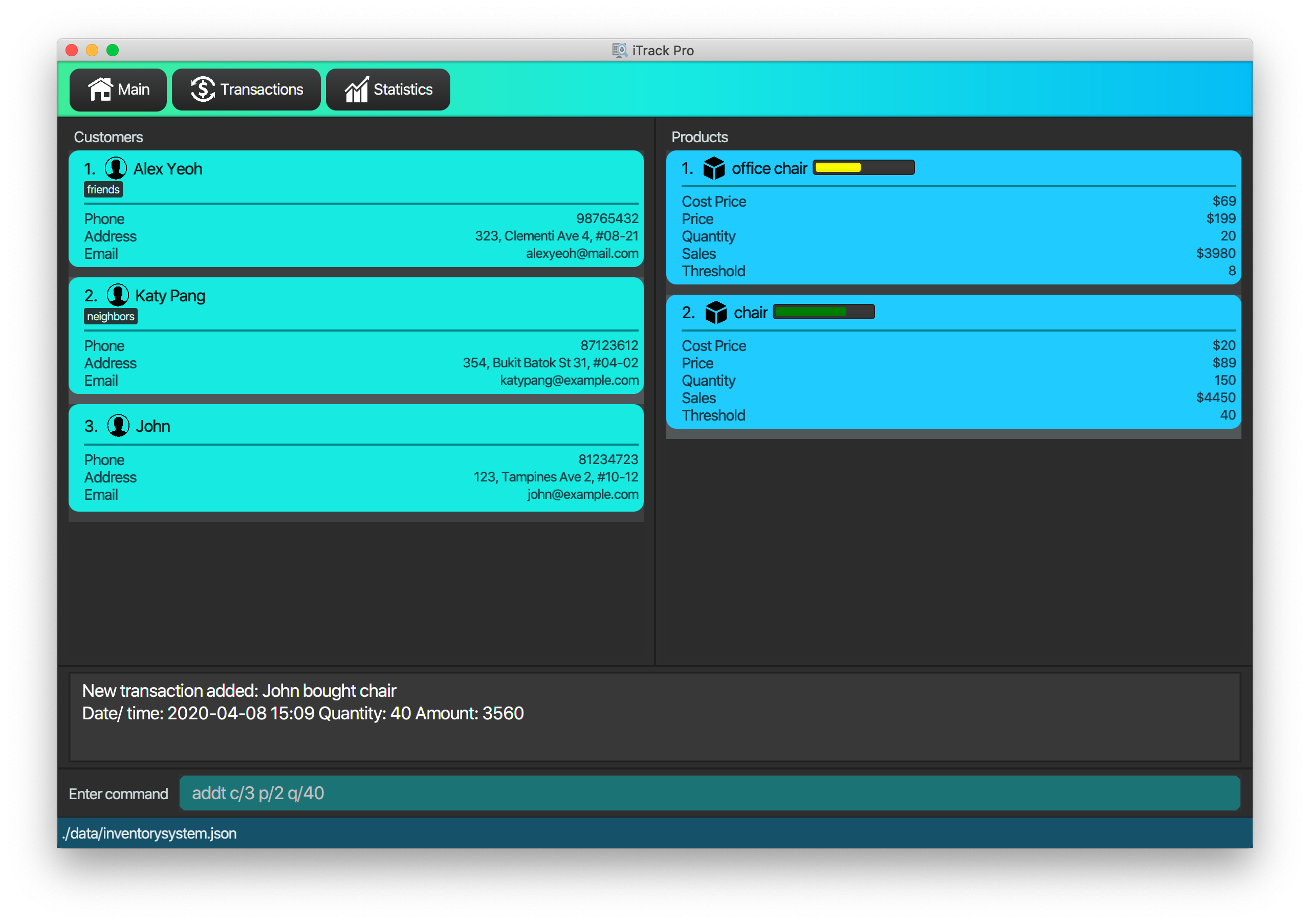
After adding transactions, the transaction list can be viewed under the transaction tab.
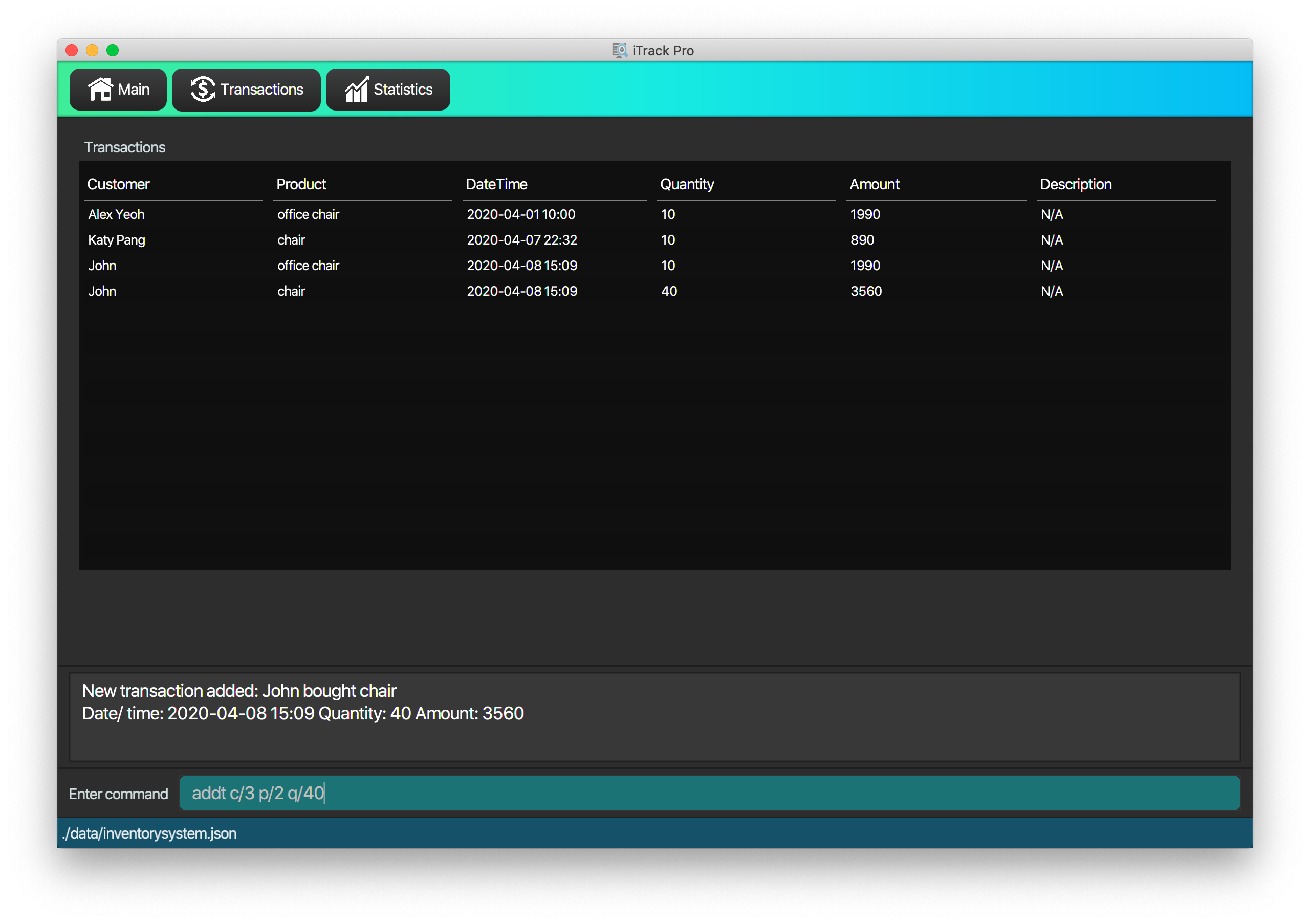
Examples:
-
addt p/1 c/10 dt/2020-02-19 19:00 q/10 m/20
Adds a transaction, where the 10th customer bought 10 of the 1st product for $20 at 2020-02-19 19:00. -
addt p/20 c/2 dt/2020-02-20 10:00 q/10 m/30 d/under discount
Adds a transaction, where the 2nd customer bought 10 of the 20th product for $30 at 2020-02-20 10:00 at an discount.
4.4.2. Listing all transactions : listt
Lists all the transactions.
Format: listt
4.4.3. Editing a transaction : editt
Edits a transaction in the system. It allows the user to edit wrong transction
with correct information.
Format: editt INDEX [p/PRODUCT_ID] [c/CUSTOMER_ID] [dt/DATE_TIME] [q/QUANTITY] [m/MONEY] [d/DESCRIPTION]
| Editting the quantity or money of a transaction will update the quantity and sales of its associated product as well. |
Examples:
-
editt 1 p/101 c/123
Edits the product id and customer id of the 1st transaction to be 101 and 123 respectively.
4.4.4. Finding transactions : findt
Finds transactions whose attributes match the given attributes.
Format: findt [p/PRODUCT_NAME [PRODUCT_NAME]…] [c/CUSTOMER_NAME [CUSTOMER_NAME]…] [dt/DATE_TIME] [m/MONEY]
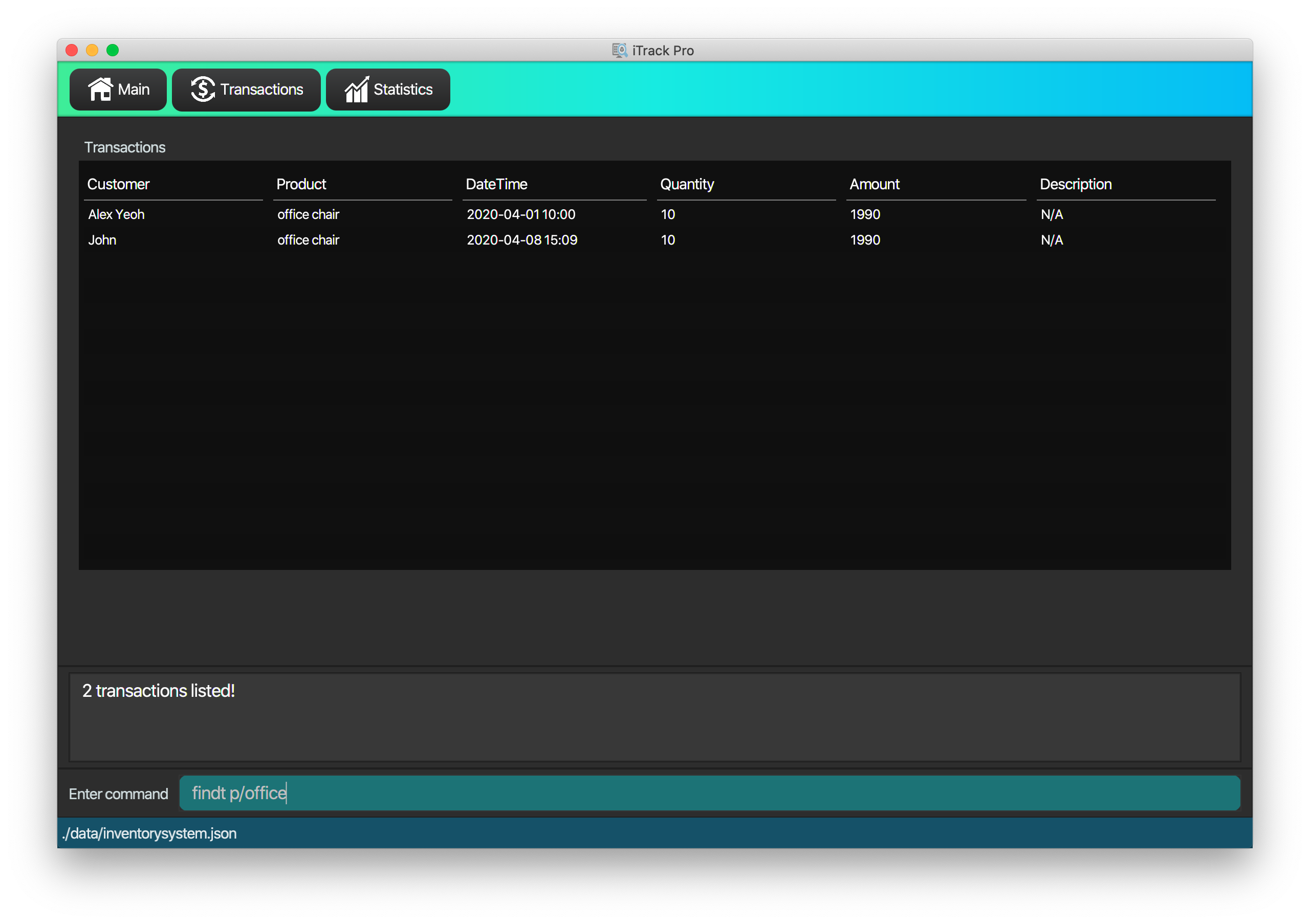
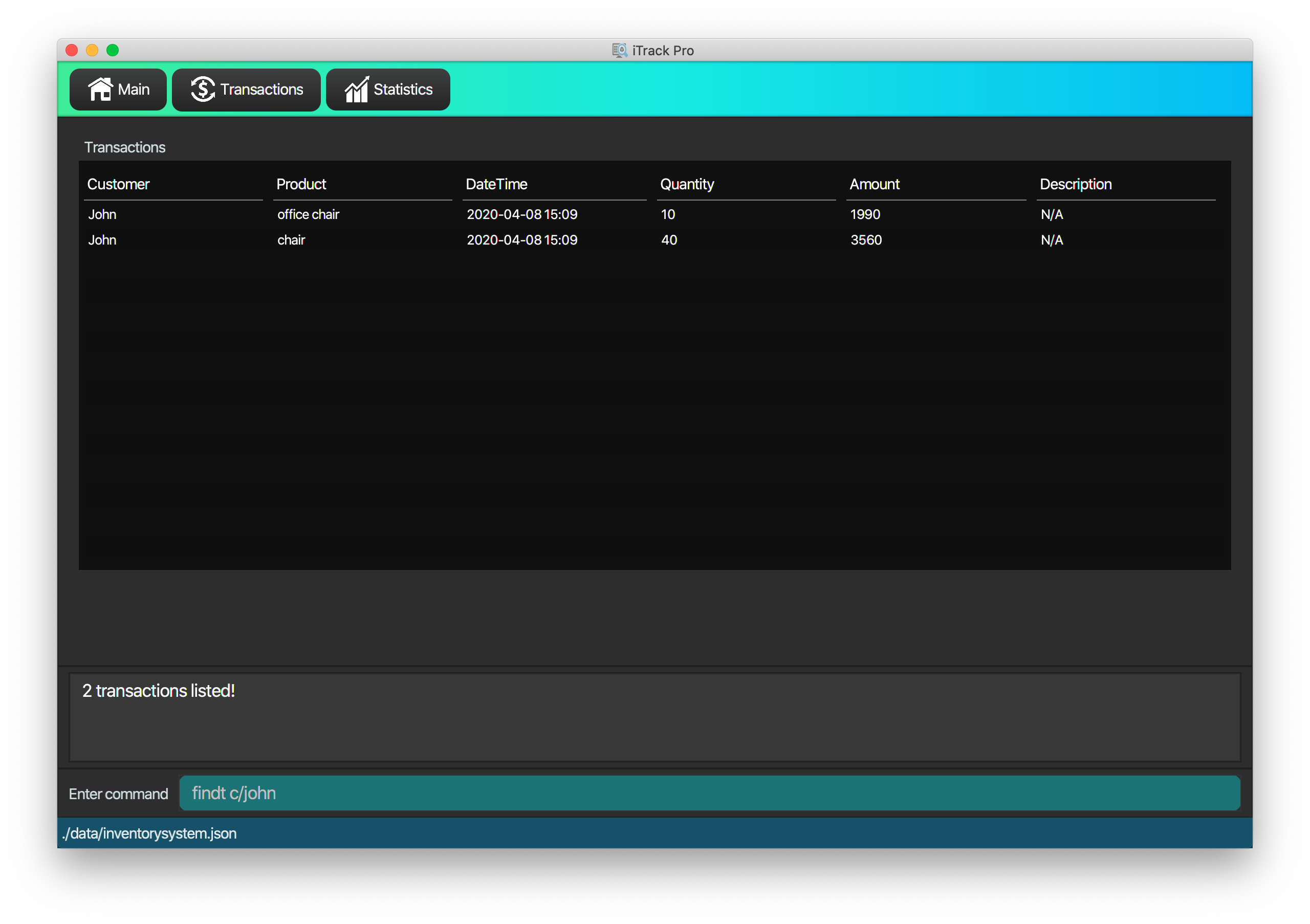
| Only product name and customer name support multiple keywords |
Examples:
-
findt p/iphone
Returns all transactions that involve the productiphone. -
findt c/bob angie
Returns all transactions that involve a customer named Bob OR a customer named Angie. -
findt dt/2020-02-07 16:00
Returns all transactions made on 7th February 2020 4pm. -
findt m/100
Returns all transactions that have an amount of 100 dollars. -
findt c/bob dt/2020-02-07 16:00
Returns all transactions that Bob made on the 7th February 2020 4pm.
4.4.5. Undo a transaction : undot
Undo the specified transaction from the system. It allows the user to remove a transaction in case he/she keyed inaccurate
information.
Format: undot INDEX
| Why undot instead of deletet? Deletet implies that transaction is only deleted but undot is more fitting as the product details will be modified too. |
| Adds the quantity in the transaction back to the product and reduces the sales of the product by transaction amount. |
Examples:
-
listt
undot 2
Undo the 2nd transaction in the displayed list. -
findt dt/2020-01-03 16:00
undot 1
Undo the 1st transaction in the results of the find command.
4.4.6. Clearing all transactions : cleart
Clears all transactions from the list of transactions.
Format: cleart
| Permanently deletes all the stored transaction data in the application. |
4.5. Statistics
User can navigate to the statistics panel by clicking on the statistics tab.

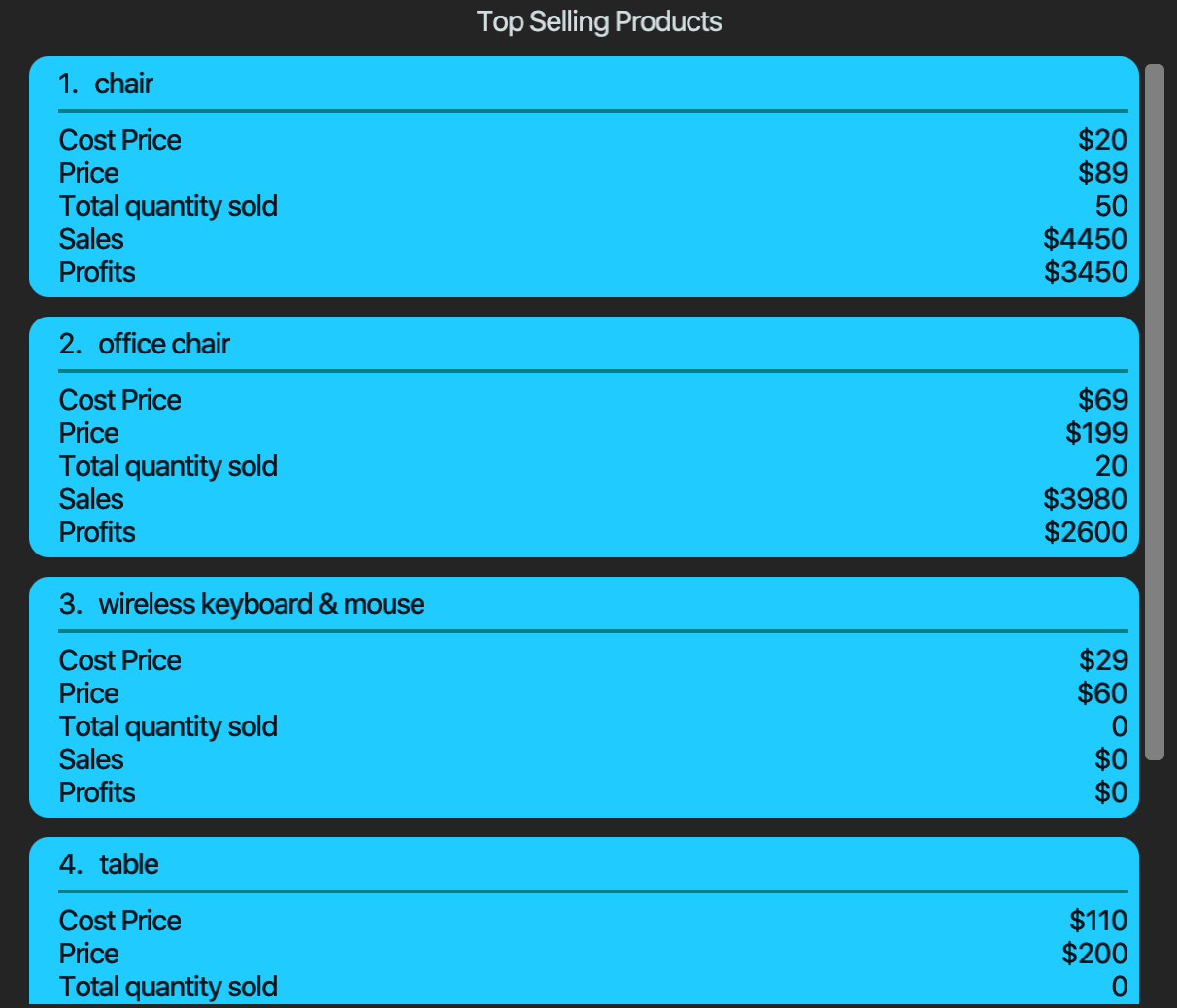
4.5.1. Viewing the top-selling and worst-selling products.
Displays and updates the top-selling and worst-selling products (sorted by profit) as transactions are made.
| This is a passive feature. |
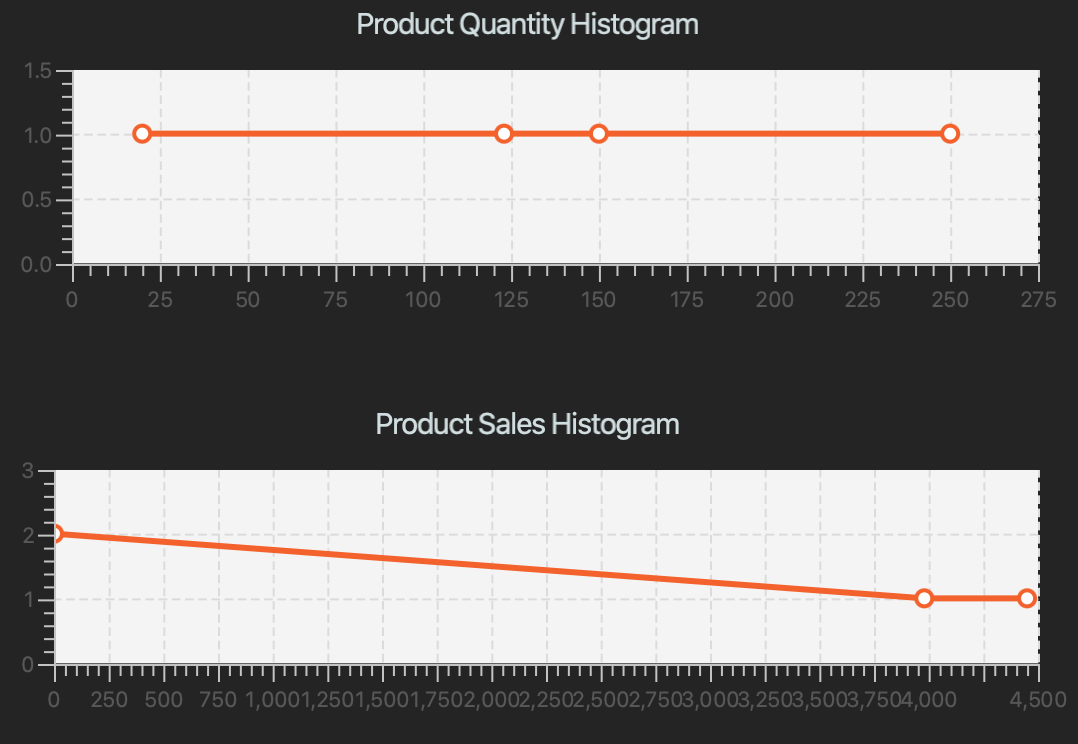
4.5.2. Viewing the product sales and quantity histogram.
Displays and updates the histogram of product sales and quantity.
Plots 2 graphs:
1. Number of products against quantity of products
2. Number of products against sales of products
| This is a passive feature. |
4.5.3. Getting the revenue made in a certain period : revenue
Gets the revenue made in a selected period. (start date to end date, both inclusive)
Format: revenue [sd/START_DATE] [ed/END_DATE]
Example:
-
revenue sd/2020-01-01 10:00 ed/2020-12-31 10:01
Returns the revenue from Jan 1 2020 10am to Dec 31 2020 10:01am
4.5.4. Getting the profit made in a certain period : profit
Gets the profit made in a selected period (start date to end date, both inclusive).
Format: profit [sd/START_DATE] [ed/END_DATE]
Example:
-
profit sd/2020-01-01 10:00 ed/2020-12-31 10:01
Returns the profit from Jan 1 2020 10am to Dec 31 2020 10:01am
4.5.5. Setting the low-inventory threshold : lowlimit
Sets the notification threshold for individual product and updates the bar indicator of the product.
Format: lowlimit p/PRODUCT_ID t/THRESHOLD
|
The default threshold represents 20% of the desired quantity. The quantity threshold can take integers up to 1000000. |
Examples:
-
lowlimit p/1 t/20
Sets the low inventory threshold for the 1st product as 20.
4.5.6. Predicting the sales for the next month : predict
Predicts sales for the next month based on sales in the previous three months
Format: predict
| The average of the profits made in the past three months is the predicted sales for next month. |
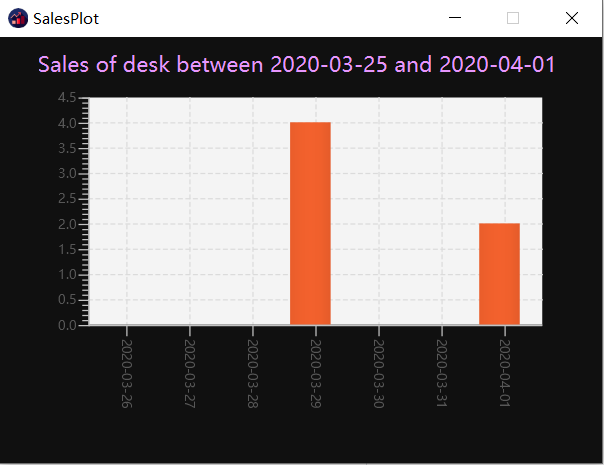
4.5.7. Plotting sales of a product: plotsales
Plots a graph with the sales of the selected product in a given time period.
Format: plotsales PRODUCT_INDEX [sd/START_DATE] [ed/END_DATE]
| The start date and end date attributes are optional. If omitted, the system will plot the last 7 days by default. |
Examples:
-
plotsales 1 sd/2020-02-20 10:00 ed/2020-02-28 10:01
Plots a graph with the sales of the selected product between 20th Feb 10am and 28th Feb 10:01am in 2020. -
plotsales 1
Plots a graph with the sales of the selected product in the past week.
5. FAQ
Q: How to delete a product?
A: First, display a list of product, e.g. listp. Then type deletep INDEX where the index refers to the index displayed in the list. Refer to Section 4.3.5, “Deleting a product : deletep”.
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous Inventory System folder.
6. Command Summary
-
Adding customer :
addc n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
e.g.addc n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 -
Listing all customers :
listc -
Editing customer information :
editc INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
e.g.editc 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com -
Finding customers :
findc [n/NAME [NAME]…] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS [ADDRESS]…]
e.g.findc n/John -
Deleting a customer :
deletec INDEX
e.g.findc n/Betsy
deletec 1 -
Clearing all customers :
clearc -
Adding a product :
addp d/DESCRIPTION pr/PRICE q/QUANTITY cp/COSTPRICE [s/SALES]
e.g.addp d/iphone x pr/1000 cp/800 q/10 -
Listing all products :
listp -
Editing a product :
editp INDEX [d/DESCRIPTION] [pr/PRICE] [cp/COSTPRICE] [q/QUANTITY] [s/SALES]
e.g.editp 1 pr/1150 q/80 -
Finding products :
findp KEYWORD [KEYWORD]…
e.g.findp black -
Deleting a product :
deletep INDEX
e.g.listp
deletep 2 -
Clearing all products :
clearp -
Adding a transaction :
addt p/PRODUCT_ID c/CUSTOMER_ID dt/DATE_TIME m/MONEY q/QUANTITY [d/DESCRIPTION]
e.g.addt p/20 c/2 dt/2020-02-20 10:00 m/30 q/10 d/under discount -
Listing all transactions :
listt -
Editing a transaction :
editt INDEX [p/PRODUCT_ID] [c/CUSTOMER_ID] [dt/DATE_TIME] [q/QUANTITY] [m/MONEY] [d/DESCRIPTION]
e.g.editt 1 p/101 c/123 -
Finding transactions :
findt [p/PRODUCT_NAME [PRODUCT_NAME]…] [c/CUSTOMER_NAME [CUSTOMER_NAME]…] [dt/DATE_TIME] [m/MONEY]
e.g.findt c/bob dt/2020-02-07 10:00 -
Undo a transaction :
undot INDEX
e.g.findt dt/2020-01-03 10:00
undot 1 -
Clearing all transactions :
cleart -
Get the revenue made in a certain period :
revenue sd/START_DATE ed/END_DATE
e.g.revenue sd/2020-01-01 10:00 ed/2020-12-12 10:01 -
Get the profit made in a certain period :
profit sd/START_DATE ed/END_DATE
e.g.profit sd/2020-01-01 10:00 ed/2020-12-12 10:01 -
Setting the low-inventory threshold :
lowlimit p/PRODUCT_ID t/THRESHOLD
e.g.lowlimit p/1 t/20 -
Predicting the sales for the next month :
predict -
Plotting sales :
plotsales PRODUCT_INDEX [sd/START_DATE] [ed/END_DATE]
e.g.plotsales 1 sd/2020-03-20 10:00 ed/2020-03-30 10:00 -
Exiting from the program :
exit -
Get help :
help
